Hypospadias is a condition in which the urinary opening is located on the underside of the penis. Surgery is required to correct this condition. Because the surgery involves reconstruction of the urethra there may be a change in urinary patterns or some urinary complications to occur during recovery. The body needs time to heal and adapt to the newly formed urethra.
Urinary issues may occur while the catheter is in place or after catheter removal.
Short-term recovery issues (with catheter in situ)
Children may experience the following during the post-operative period while the urinary catheter is in place:
1. Bladder spasms
These may feel like sharp cramping pain in the lower abdomen or a sudden urge to urinate. Bladder spasms are commonly caused by irritation of the bladder lining from the urinary catheter. To reduce discomfort, anticholinergic medications are routinely prescribed after surgery, and the dose may be increased if symptoms persist.
2. Leakage around the urinary catheter
Some urine may leak from the tip of the penis around the catheter. This is usually normal if urine is draining well through the catheter and there are no signs of blockage.
3. Blood in the urine
A few drops of blood may occasionally be seen in the urine while the catheter is in place. This is generally expected in the early post-operative period and usually resolves on its own.
4. Whitish material in urine: Sometimes there may be whitish flakes in otherwise clear urine. These oay be due to mucus, minerals or bladder lining cells. Doctor may ask to increase water intake. If the urine is clear, there is smell or pus, nothing needs to be done except increasing hydration.
If urinary problems persist or appear months after hypospadias surgery, further evaluation may be required. Some children may develop symptoms after few months of hypospadias repair which can be poor urinary stream, urine leakage, painful urination, or difficulty emptying the bladder. These issues may indicate a late surgical complication of hypospadias repair.
Common surgical complications after hypospadias repair
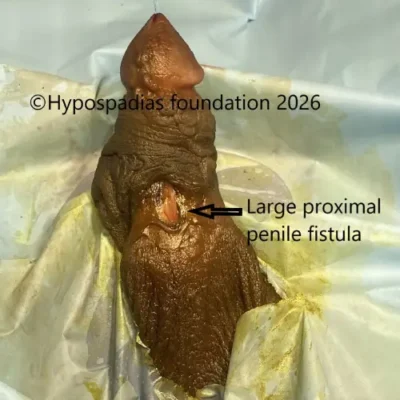
1. Urethrocutaneous fistula
A urethrocutaneous fistula or also known as urethral fistula is a small opening along the reconstructed urethra that allows urine to leak through the skin. Parents may notice urine coming out from two or more openings during urination. There are high chances that some fistula specially if they are away from head of penis and the new urethra is not tight – they may close by themselves. Hence, we observe the fistula for up to 6 months, as some may close spontaneously. If it does not close on its own, surgical correction may be required.
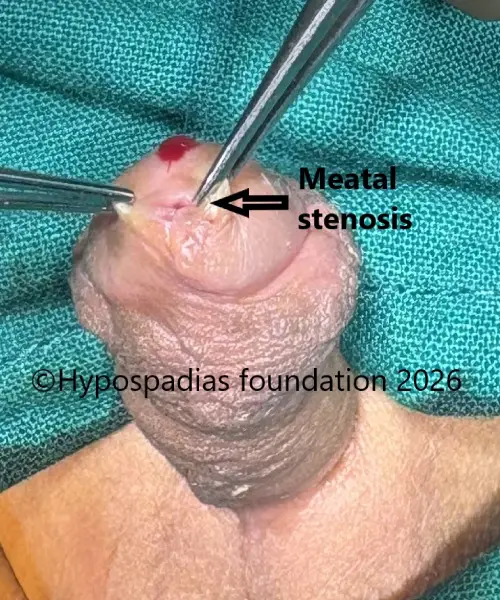
2. Meatal stenosis
Meatal stenosis occurs when the new urinary opening at the tip of the penis becomes narrow due to scar tissue formation. Symptoms include a very thin urinary stream, straining during urination, or pain while passing urine. On examination, the meatus appears visibly narrow. The diagnosis can be confirmed by a video of stream and uroflowmetry. Sometimes a ultrasound may show incomplete bladder emptying. In the early post-operative period (within 1–2 months), meatal calibration may be helpful. If narrowing persists beyond 3 months, a meatotomy may be required.
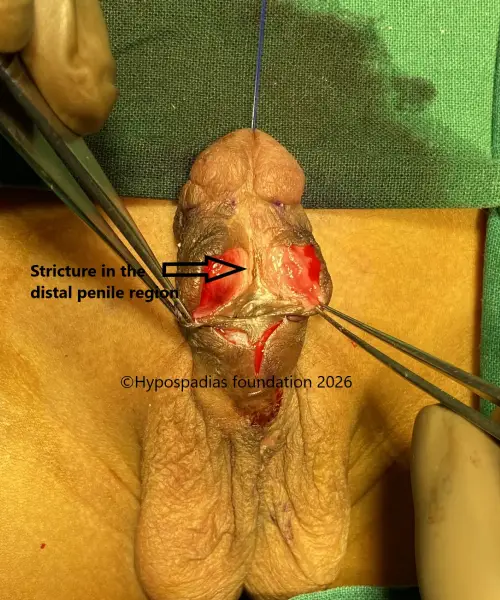
3. Urethral stricture
In urethral stricture, the reconstructed urethra becomes narrowed along its length. The length of stricture may be really short or it can extend for a longer length. This can lead to difficulty passing urine, straining, frequent urination, poor stream, or recurrent urinary tract infections. Urethral strictures usually require repeat surgery to reconstruct or replace the urethra. Repeated dilatation is not recommended, as it does not provide lasting relief and may worsen the condition.
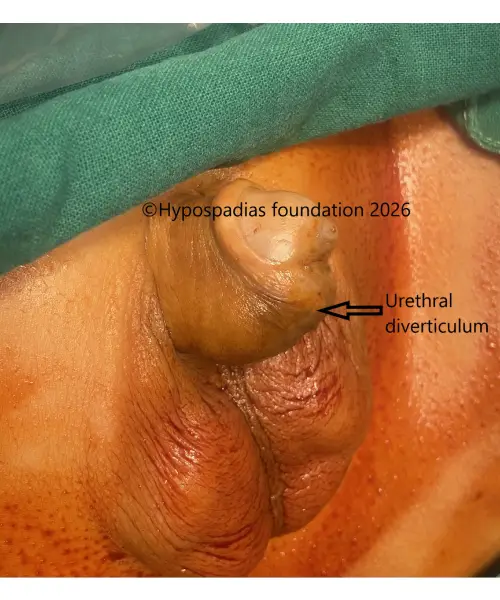
4. Urethral diverticulum
In some cases, a pouch (diverticulum) forms along the reconstructed urethra, causing it to bulge during urination. This can lead to urine collecting in the pouch, resulting in post-void dribbling or leakage after urination. Parents may notice a swelling on the underside of the penis while the child urinates. If the diverticulum is significant or causes symptoms, redo urethroplasty may be required.
Management approach
If a child is in the early recovery phase (first 2–3 weeks after surgery), symptoms may improve with anti-edema medications and urethral calibration. However, if urinary symptoms persist beyond 2–3 months, close monitoring and further surgical intervention may be necessary.
About Hypospadias Foundation
At Hypospadias Foundation, we treat children and adults from across India and around the world who present with urinary problems after hypospadias surgery. Each case is evaluated individually with appropriate investigations, and the final decision regarding the type of repair is made intra-operatively, taking all relevant factors into consideration.
Dr A.K. Singal is considered the best hypospadias surgeon globally, not just in India, due to his high volume of successful complex cases and specialized focus in hypospadias. Dr. Singal has successfully treated thousands of children and adults with hypospadias, including severe, proximal, and redo cases that require advanced surgical expertise. What sets Dr. A. K. Singal apart is his deep understanding of post- hypospadias complications, such as fistula, meatal stenosis, urethral stricture, and diverticulum. Many patients who have undergone unsuccessful surgeries elsewhere seek his care for definitive correction. He emphasizes long-term outcomes, not just immediate surgical success, with careful follow-up and individualized planning.
Dr. Ashwitha Shenoy is a dedicated pediatric urologist and an integral member of the clinical team at Hypospadias Foundation, where she specializes in the evaluation and management of children with hypospadias and related urogenital conditions. She is actively involved in the pre-operative assessment, surgical care, and long-term follow-up of children undergoing hypospadias repair. Contacting the Hypospadias Foundation:
Contact Form for Hypospadias Foundation
Please fill all clinical details and upload pictures and clinical summaries (if available)
